Goal
Explains the integration between ERP and EWM from the system landscape, organization structure and process view point.
Demonstration videos explaining the integration between ERP & EWM.
Overview
Integration between ERP and EWM can broadly be divided into 3 levels. Most of these settings are required even with EWM embedded in SAP S/4HANA . The details are a little different, but in general, the requirements are the same.

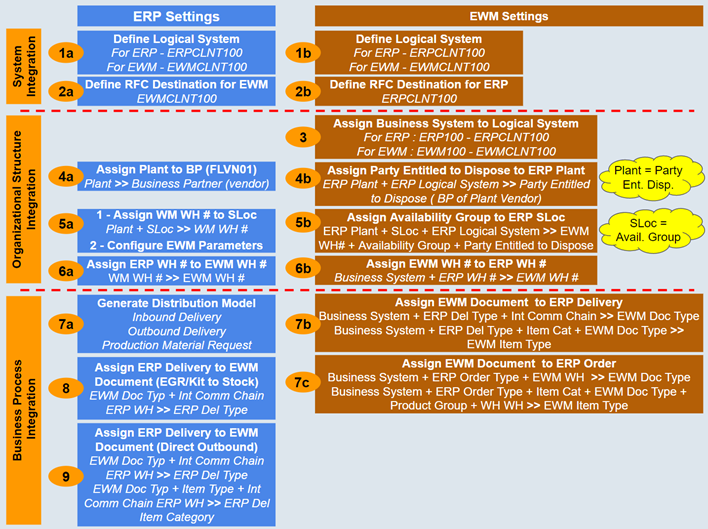
Details are explained in the following sections with references to the numbers assigned to settings.
System Landscape Integration
System level integration is not really EWM specific but this is required in general for the communication between two SAP systems.
ERP Settings
1a. Define a Logical System
Define a logical system for each system and assign it to the client being used in each server. In our example, we assign S1TCLNT101 to client 101 of the SAP ERP system, and assign SEWCLNT010 to client 010 of the SAP EWM system.
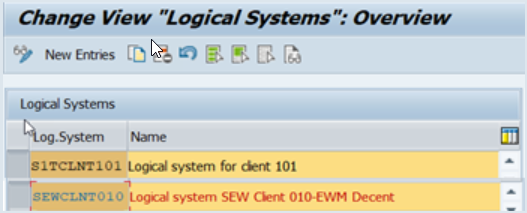

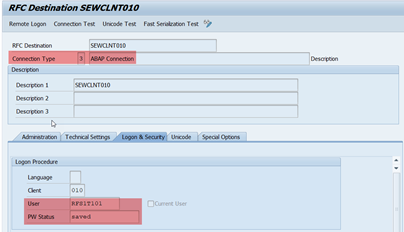
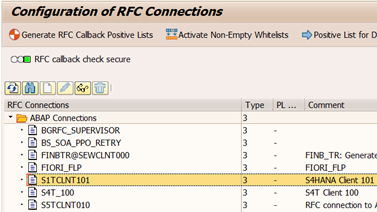
2a. Define RFC Destinations
Define RFC destinations with the same name as the logical systems (in our example S1TCLNT101 and SEWCLNT010).
Note: Define an RFC user in each target system / client before this step.
EMW Settings
1b. Define a Logical System
Define a logical system for each system and assign it to the client being used in each server.
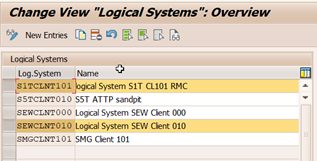
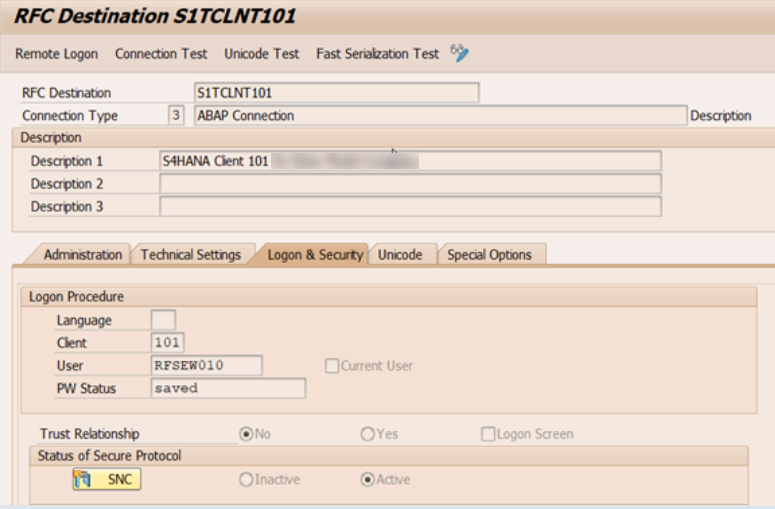
2b. Define RFC Destinations
Define RFC destinations with the same name as the logical systems (in our example S1TCLNT101 and SEWCLNT010).
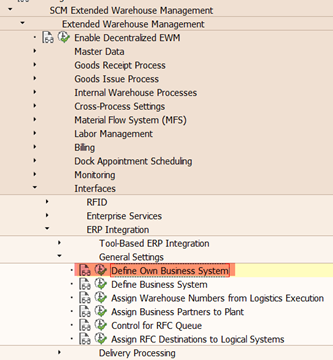
Additional Settings – Define Business System
A business system will be defined for the EWM (own business system) and for each ERP system that is connected to EWM system. The SAP EWM system stores the business system in the document flow tables of the cross-system and cross partner document flow and helps to determine to which ERP system a document belongs to.
Business systems is mapped to their corresponding logical systems, because the delivery documents sent from the SAP ERP system to the SAP EWM system contain only the logical system number of the SAP ERP system. This mapping helps to determine the business system based on logical system so that the warehouse request document in EWM can be updated with the corresponding business system.
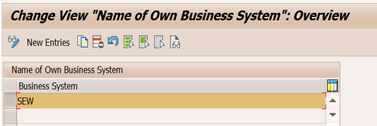
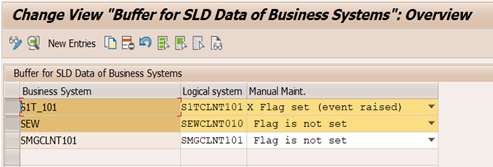
Following example shows the business system information in warehouse request document

Organization Structure Integration
These settings establish the connection between the elements of organization structure (plant, storage location, warehouse) of ERP and EWM systems.
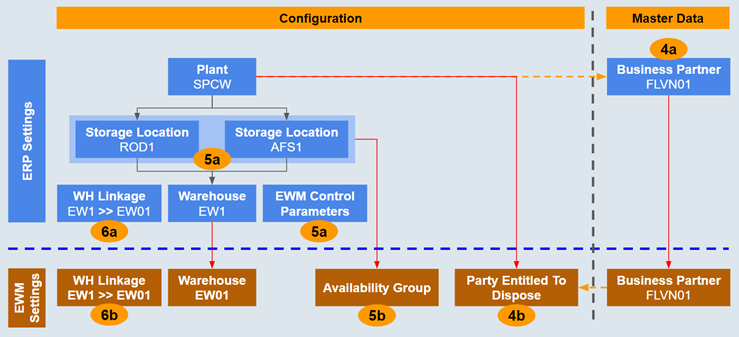
ERP Settings
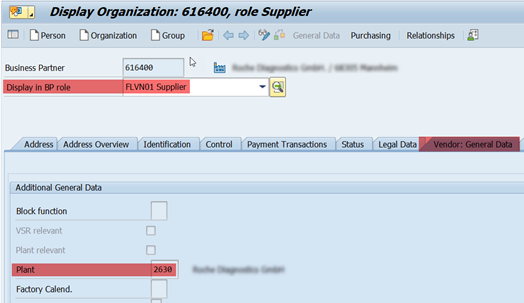
4a. Assign Plant to Business Partner (with role FLVN01-Vendor)
From a stock management perspective, plant does not exists in EWM system. ERP plant is represented by ‘Party Entitled to Dispose’ in EWM stock details. Party Entitled to Dispose is nothing but a Business Partner (with role FLVN01-Vendor) that is transferred from the ERP for which Plant is assigned in the general data.( see 4b)
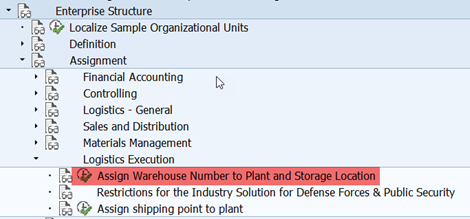
5a-1. Activating Warehouse Management for Plant and Storage Location
An intermediate warehouse number is created and it is assigned to the combination of plant and storage locations for which EWM is required. This warehouse number is the logical representation of EWM warehouse in ERP system.
Note: Do not create ERP warehouse by copying template warehouse, as it does not require all the structural elements of ERP warehouse.
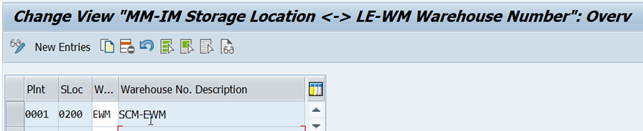
5a-2. Configure EWM Control Parameters
Warehouse is activated as EWM warehouse and a distribution model is created to ensure the transfer of SAP ERP delivery data to and from the SAP EWM system.
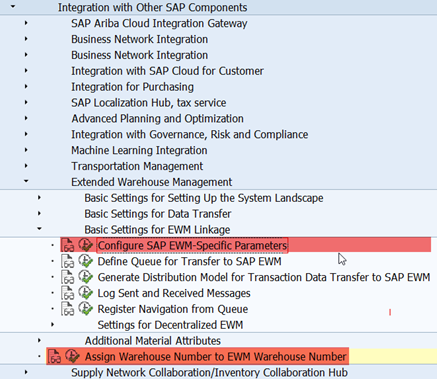
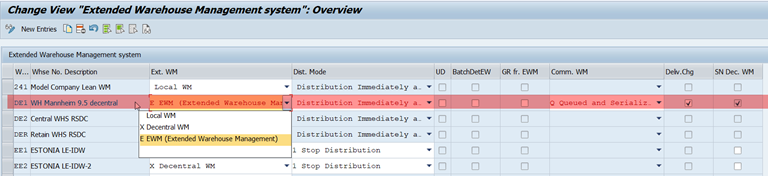
At the activation of the warehouse as EWM warehouse, the following settings can be chosen.
- Comm. WM (Communication external WM)
The correct entry for EWM is Queued and Serialized Asynchronous RFC.
- UD (Unchecked Deliveries)
This setting controls if unchecked deliveries are to be distributed. An unchecked delivery is a delivery with a reduced scope of check. This reduced scope of check refers mainly to the availability checks, but can also affect other checks. CRM can create unchecked deliveries in ERP.
- Dist. Mode (Distribution Mode)
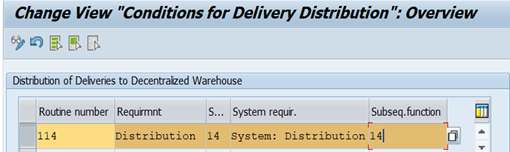
The setting controls if a delivery is distributed immediately at creation (default entry) or not (Stop distribution). If the distribution is not done immediately, you trigger the distribution in the Outbound Delivery Monitor (For Distribution) or with transaction VL06D. You can override this default setting through the entry in the Distribution Mode of the delivery type. Additionally a form routine controls the distribution. By manipulating this form routine, you can implement specific checks and requirements. You can find this by using the transaction code VOFM and choosing Requirements > Subsequent functions > Distribution.
- SN Dec. WM (Allow Serial Numbers in Decentralized WMS)
Once you have selected that the warehouse number is an EWM warehouse, this indicator is set and not changeable anymore. It means that you can work with serial numbers in EWM, the details are controlled by the serial number profiles.
- BatchDetEW (Batch Determination in EWM via Batch Attribute Replication)
This indicator controls the behavior of the automatic batch determination in ERP outbound deliveries.
- GR fr. EWM only (Goods Receipt from EWM Only)
This indicator enables you to control whether the process of posting the goods receipt for a manufacturing order into an EWM-managed warehouse can be started from both ERP and EWM or from EWM only.
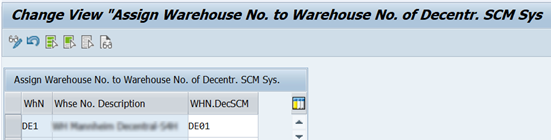
6a. Linking ERP Warehouse to EWM Warehouse
A link is established between the logical warehouse number of ERP and its counterpart in EWM.
EWM Settings
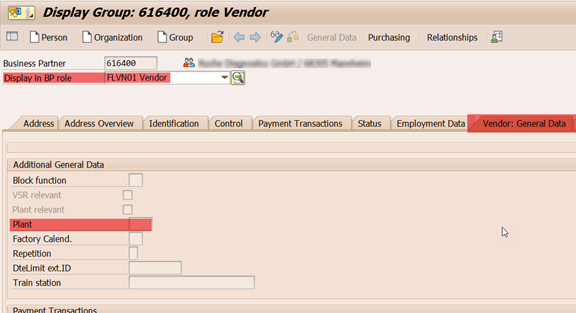
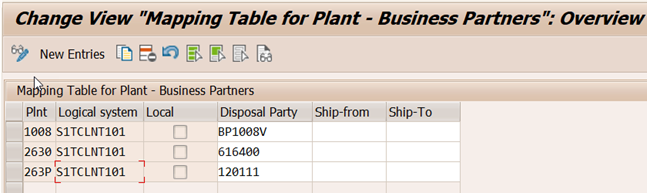
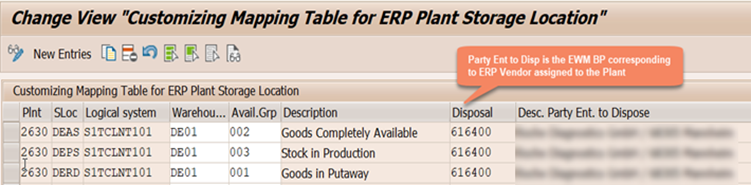
4b. Assign Party Entitled to Dispose to ERP Plant
From a stock management perspective, plant does not exists in EWM system. ERP plant in EWM is represented by Party Entitled to Dispose in EWM stock details. Party Entitled to Dispose is nothing but a Business Partner (with role FLVN01-Vendor) that is transferred from the ERP for which Plant is assigned in the general data.( see 4a)
5b. Assign Availability Group to ERP Storage Locations
From an organizational structure perspective, storage locations do not exists in EWM system. Availability Group is used to map ERP storage locations, which in turn is linked EWM stock type and ERP stock type (location independent stock type). ( see Availability Group for more information)

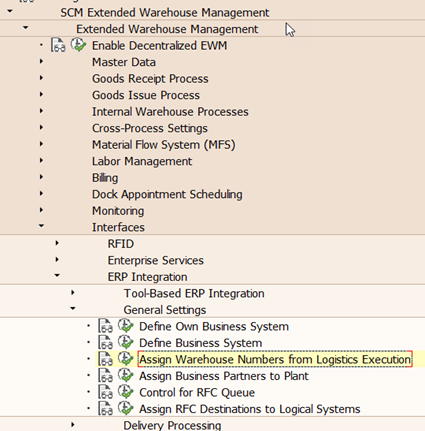
6b. Linking ERP Warehouse to EWM Warehouse
A link is established between the EWM warehouse number and its logical counterpart in ERP.
Note: This mapping is required in decentralized as well as in embedded EWM.
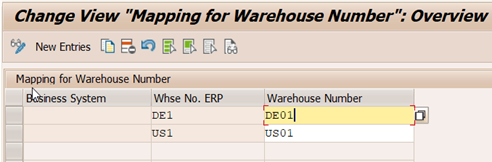
Business System plays critical role if decentral EWM system is connected to more than one ERP systems. It may be possible that the same ERP warehouse number is available in more than one ERP system that is connected to decentral EWM system. Business system helps to maintain uniqueness in such cases.
Business Process Integration
These settings establish connection between the elements of business processes (inbound, outbound, production) of ERP and EWM systems. Business process integration is achieved via delivery documents.
ERP Settings
7a. Generate Distribution Model
Distribution models required to transfer business documents such as deliveries (inbound, outbound, posting change) and process/production orders (as Production Material Request).
For creating the distribution model enter –
- The ERP warehouse number
- The logical system key of the EWM system
- A distribution model view
The distribution model view is how you can later locate the distribution model in the transaction BD64 – Maintenance of Distribution Model.
You can select any of the following as Objects for the distribution model:
- Inbound Delivery
- Outbound Delivery
- Production Material Request
- All
It is not helpful to have separate models, so All is the correct choice. Only in case you would know that the advanced production integration will not be used, it could make sense to select Inbound Delivery and Outbound Delivery separately.

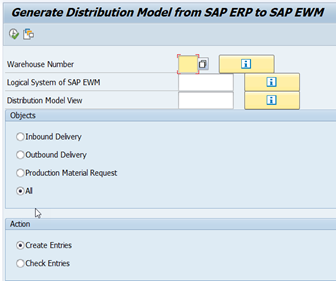
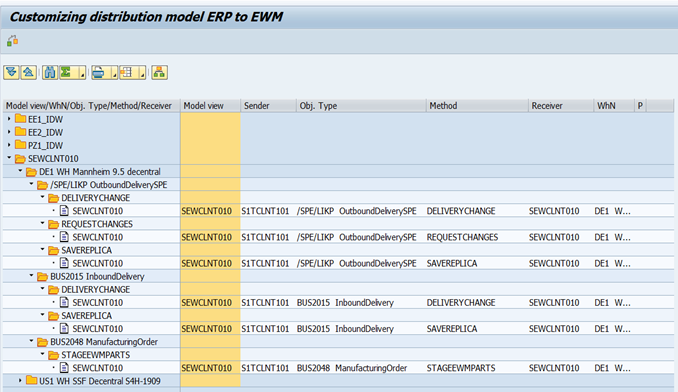
Following is the display of distribution model in BD64

8. Assign ERP Delivery to EWM Document (Inbound Delivery)
In certain business scenarios such as kit-to-stock and GR for expected goods receipt, it is possible to push the deliveries from EWM directly which will then create corresponding inbound delivery document in ERP.

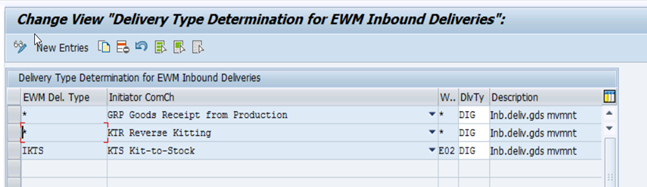
9. Assign ERP Delivery to EWM Document (Direct Outbound)
In certain business scenarios such as direct sales (without sales orders), GI for cost center, scrapping, kit-to-stock / reverse kitting, immediate deliveries, it is possible to push the deliveries from EWM directly which will then create corresponding outbound delivery document in ERP.

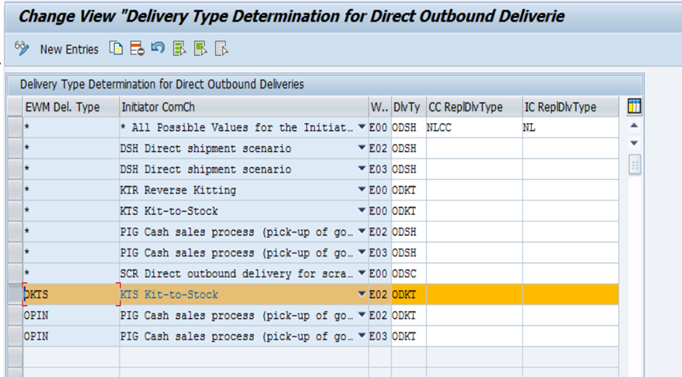
EWM Settings
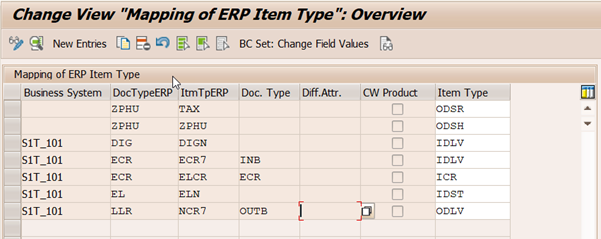
7b. Assign EWM Document to ERP Delivery
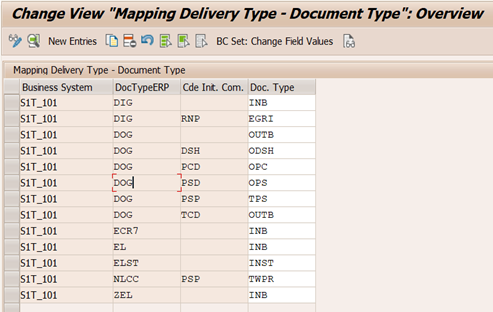
ERP Delivery Type and Item Category are assigned to EWM Document Type and Item Type respectively.
Assign EWM Delivery Type
EWM Delivery Type is assigned to ERP Delivery as show in the following picture.

Business System plays significant role if more than one ERP system is connected to decentral EWM.
The Code for Initiator of a Communication Chain is an additional key, which helps to distinguish different processes. This is necessary as sometimes the determination of the document type in ERP is very simple or because additional information is determined within the context of the received delivery information.
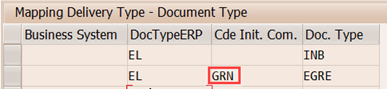
In this example, ERP delivery type remains same for normal and expected goods receipt but from EWM context different Document Type required, which is differentiated by Code for Initiator of a Communication Chain.
In a decentralized EWM system, the “EWM delivery document type” would be an Inbound Delivery Notification, an Outbound Delivery Request, or a Posting Order Request.
Since EWM 9.5 or with a decentralized EWM based on SAP S/4HANA it is possible to “skip” these requests or notifications. The path to do this is EWM Customizing, SCM Extended Warehouse Management > Extended Warehouse Management > Interfaces > ERP Integration > Delivery Processing > Skip Request for Messages from ERP (for a SCM based EWM) or SCM Extended Warehouse Management > Extended Warehouse Management > Interfaces > ERP Integrations > ERP Integration for Decentralized EWM > Skip Request for Messages from ERP (for a SAP SAP S/4HANA-based EWM). This has certain consequences, so you should read the documentation for this Customizing topic before deactivation.
In a SAP S/4HANA embedded EWM these interim documents are generally not created.

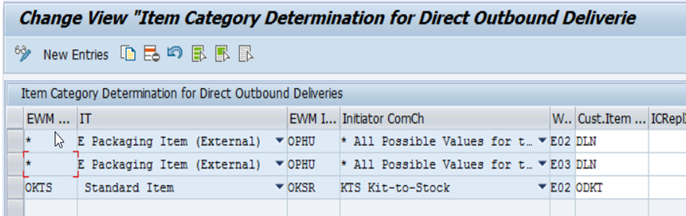
Assign EWM Delivery Item Type
EWM Item Type is assigned to ERP Delivery Item category as show in the following picture.

Differentiation Attribute for Item Type Mapping is an additional key, which helps to distinguish different processes. This is necessary as sometimes the determination of the item category in ERP is very simple or because additional information is determined within the context of the received delivery information.
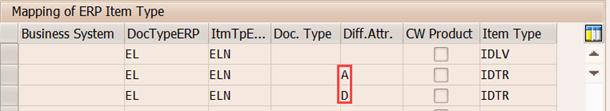
In this example, ERP item category remains same for normal GR and GR against different scenarios of stock transfer but form EWM context different Item Type is required, which is differentiated by Differentiation Attribute.
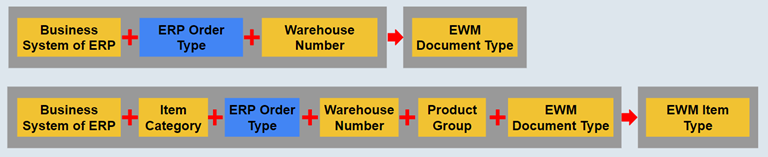
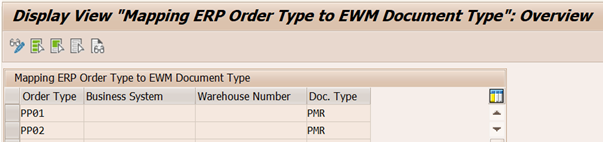
7c. Assign EWM Document to ERP Order (Manufacturing)
EWM production material request (PMR) Document Type and Item Type are assigned to ERP manufacturing Order Type as show in the following picture.

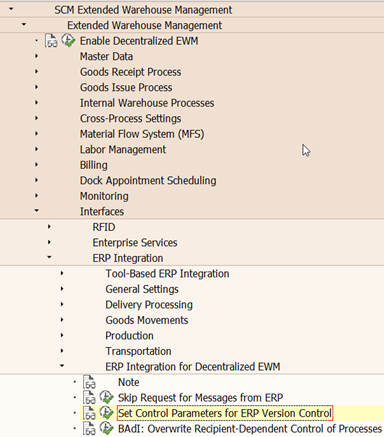
Additional Settings – Control Parameters for ERP Version Control
Once the connection between ERP and EWM system is established, set control parameters to indicate various data transfer options between the systems. These settings are dependent on the business system of the connected SAP ERP system, and the release and support package.
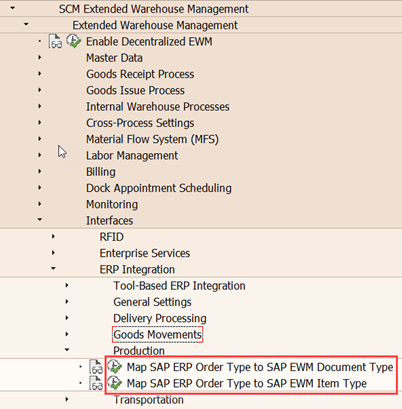
This table is in Customizing for SCM Extended Warehouse Management under
Extended Warehouse Management > Interfaces > ERP Integration > General Settings > Set Control Parameters for ERP Version Control
or
Extended Warehouse Management > Interfaces > ERP Integration > ERP Integration for Decentralized EWM > Set Control Parameters for ERP Version Control (for a SAP S/4HANA-based EWM). SAP provides standard entries for this table.
Note:
It is actually optional to create an entry for the ERP system in this table. If there no entry in your EWM system. EWM will behave as if the highest possible ERP enhancement package were connected. This table is not used for embedded EWM.