SAP S/4 HANA Treasury – Trade Finance – Overview and Configuration
Global and Local Banks support international trade through a wide range of products that help their customers manage their international payments and associated risks, and provide needed working capital. The term “trade finance” is generally reserved for bank products that are specifically linked to underlying international trade transactions (exports or imports). As such, a working capital loan not specifically tied to trade is generally not included in this definition. Trade finance products typically carry short-term maturities, although they trade in capital.

One of the most common and standardized forms of bank-intermediated trade finance is a letter of credit (L/C). L/Cs reduce payment risk by providing a framework under which a bank makes (or guarantees) the payment to an exporter on behalf of an importer once delivery of goods is confirmed through the presentation of appropriate documents. SAP has introduced new products to cover the trade finance in S/4HANA Treasury.
- Letter of Credit
- Bank Guarantee
- Standby Letter of Credit
The Trade Finance Management process generally covers the creation of financial transactions and executes payments for fees and cash collateral for bank guarantee issuing. For further processing, the roll over and termination of transactions is possible. All of the financial transactions can be monitored and reported in S/4HANA.
Functions and Business Values Available in SAP S/4HANA Treasury For Trade Finance
Master Data Management
- Master data for Letter of Credit, Bank Guarantee, and Standby Letter of Credit
- Support Master Data Management for both buyer and seller
- Customizable user interface with many tab screens
- Comprehensive and Flexible document management for Letter of Credit
Lifecycle Management
- Status Management with different steps, Contract – Settlement – Rollover – Termination
- Customer Specific workflow can be configured
- Full support of presentation and payment process for letter of Credit
Integration
- Represented as a new product category in TRM – covering Transaction and Position Management
- Integration with Accounting and Cash Management
- Full support of Loan generation out of Letter of Credit Directly
- Integration with Facility
- Integration with Credit Risk Analyzer
- Support the combined usage of the facility and cash collateral for the Applicant.
- Provide comprehensive BAPI’s for Transaction Management
Communication
- Integrated in the correspondence Framework
- SWIFT Messages with respective sub-messages
Trade Finance Customization
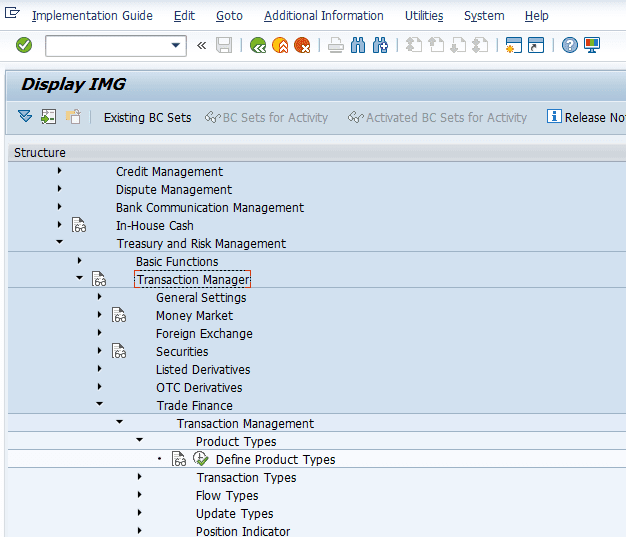
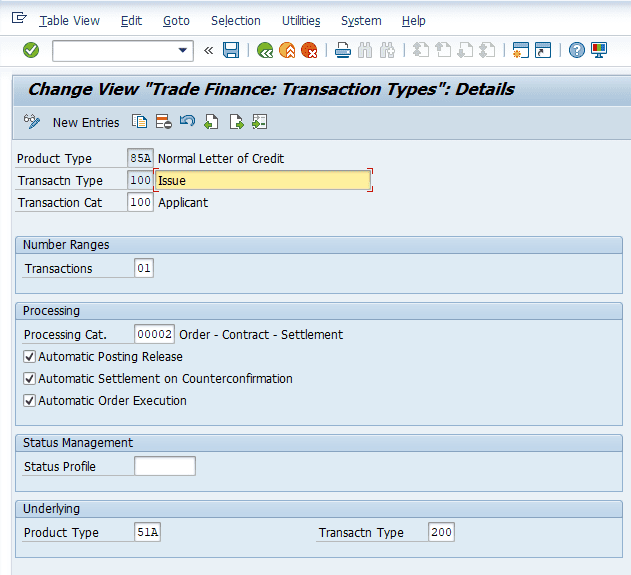
We will start by configuring the Trade finance instrument in S/4HANA . In this activity, you can maintain the product type as per your requirements. This will help you differentiate between your financial transactions and the transaction types used for each product type and their assignment.
In SAP S/4HANA Trade Finance, 2 product type categories available, namely:
- 850 – Letter of Credit
- 860 – Bank Guarantee
An underlying transaction is used in presentation to create an import bill advance for buyers or create export bills negotiation loans for sellers.
Defining Product type
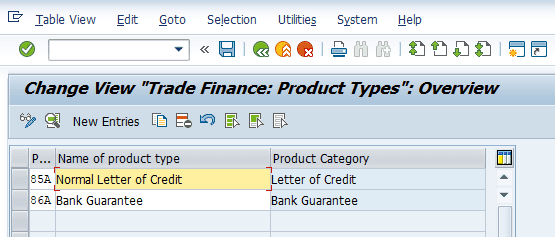 Defining Transaction Types
Defining Transaction Types
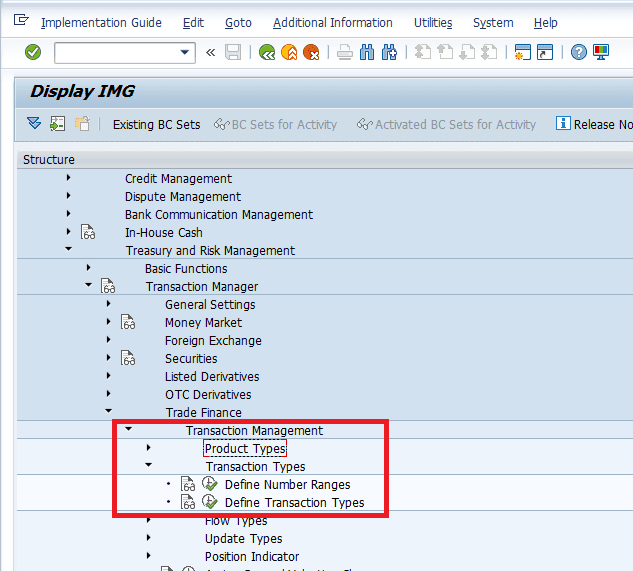
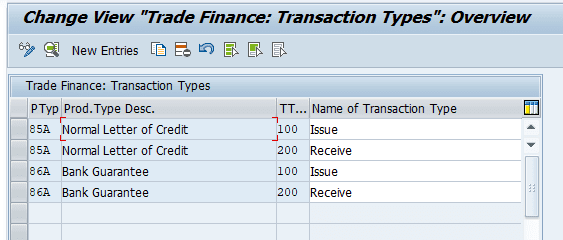
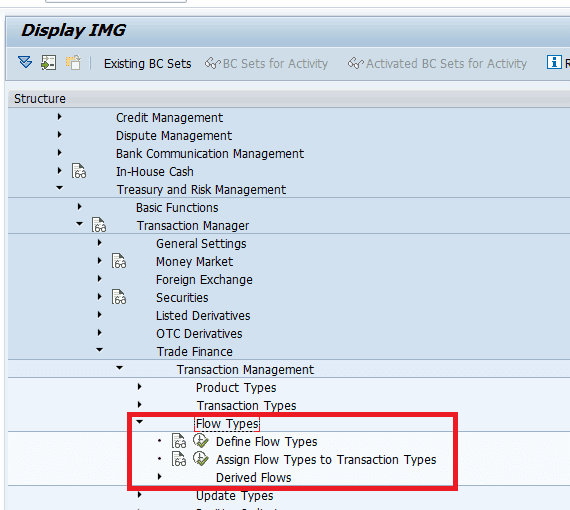
 Defining Flow types
Defining Flow types
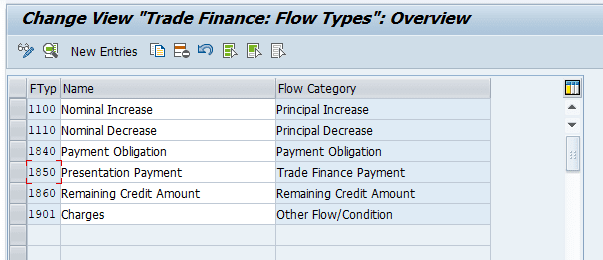
In the S/4HANA Trade Finance area the following flow categories are available:
- 10 – Principal Increase
- 11 – Principal Decrease
- 84 – Payment Obligation
- 85 – Trade Finance payment
- 86 – Remaining credit amount
- 90 – Other flow condition
- 91 – Collateral
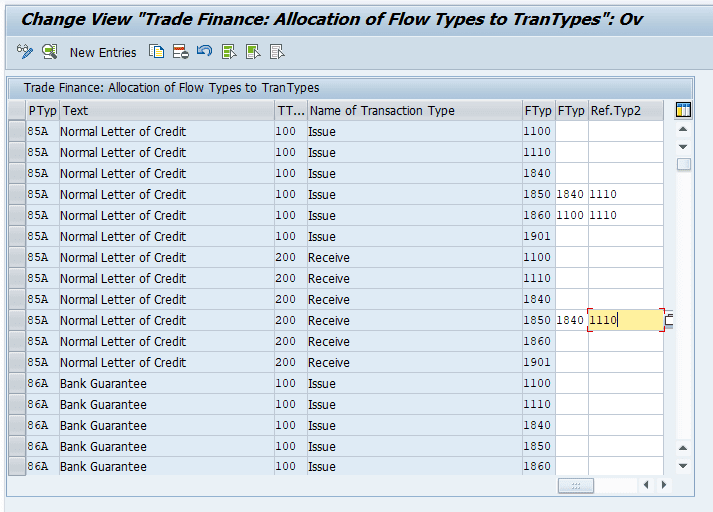
Reference Flow types
- Flow category 85 could be assigned with 84 in reference type 1 and flow category 11 in reference type 2, which is assigned for the same product type and transaction type.
- Flow category 86 could be assigned with 10 in reference type 1 and flow category 11 in reference type 2, which is assigned for the same product type and transaction type.
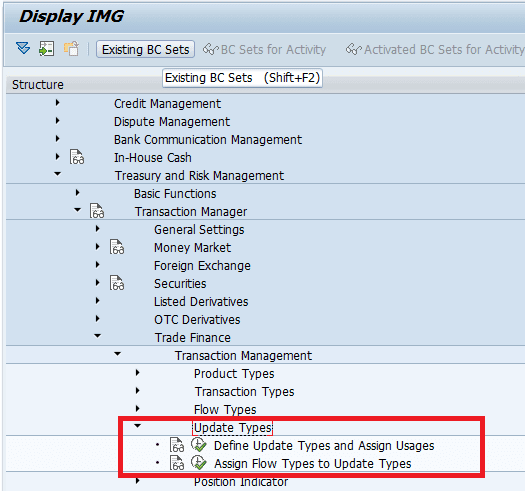
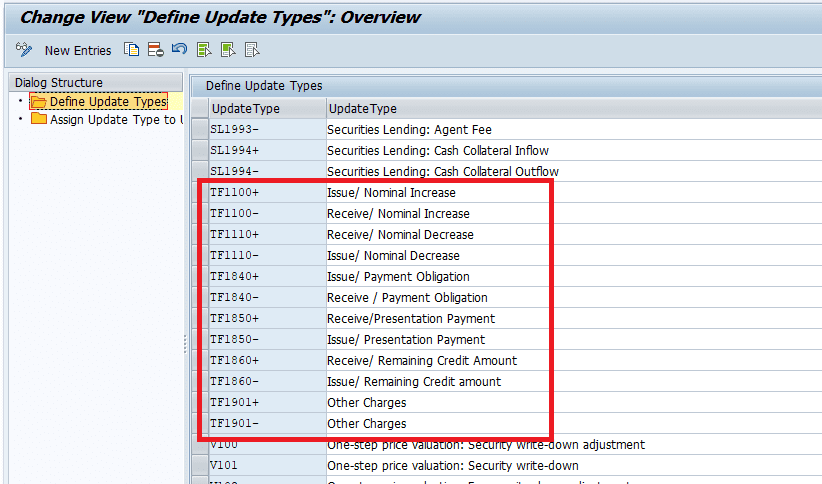
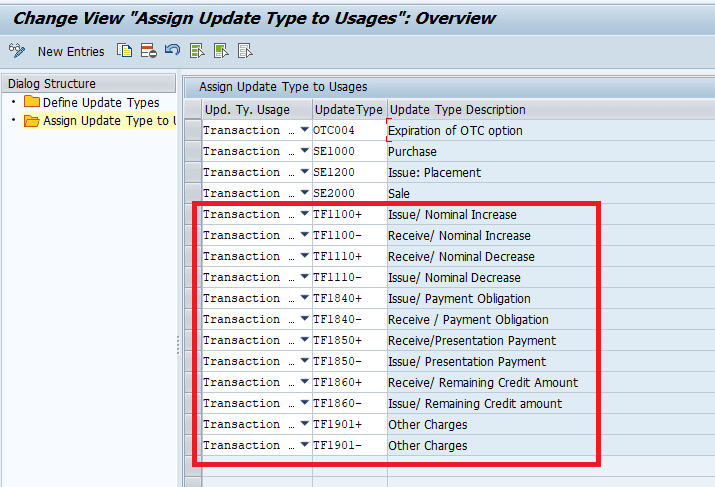
 Defining Update types
Defining Update types
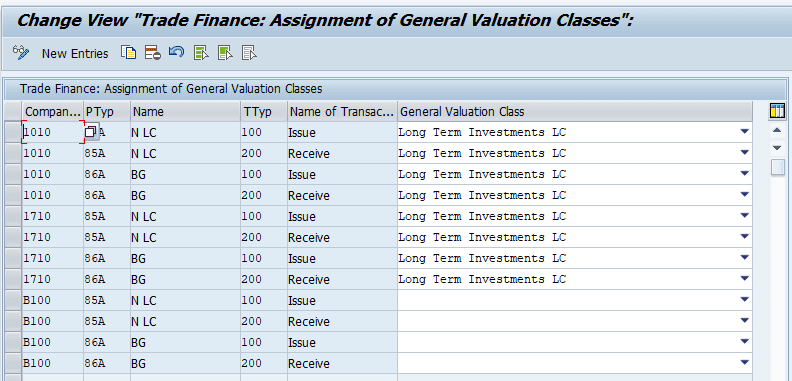
 Assigning General Valuation class
Assigning General Valuation class
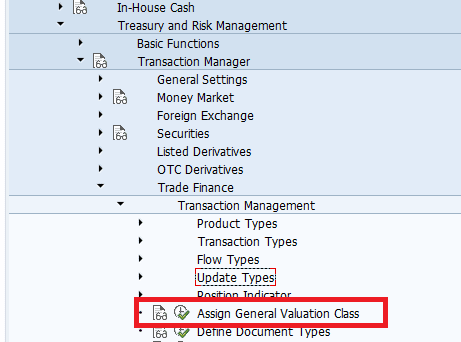
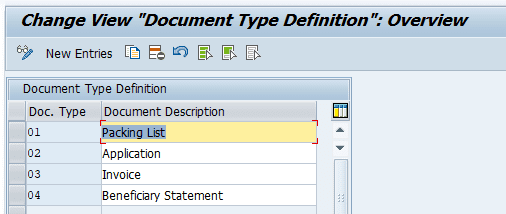
 Defining Document type
Defining Document type
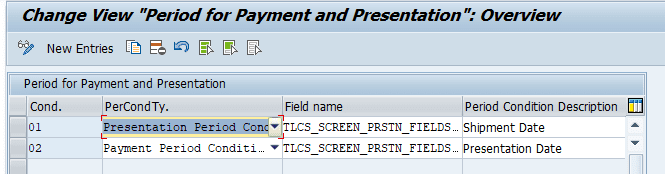
 Defining Conditions for Payment and Presentation Period
Defining Conditions for Payment and Presentation Period
In this Customizing activity, you define conditions for presentation and payment period.
The system provides one default presentation period condition Shipment Date, and one default payment period condition Presentation Date. You can define other presentation and payment period conditions based on your needs.
 Defining Rejection Reasons for L/C Presentation
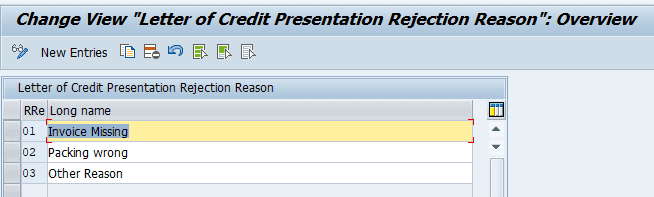
Defining Rejection Reasons for L/C Presentation
In this Customizing activity, you define rejection reasons for L/C presentations by assigning a reason code and a description that you can select later when you reject a presentation.
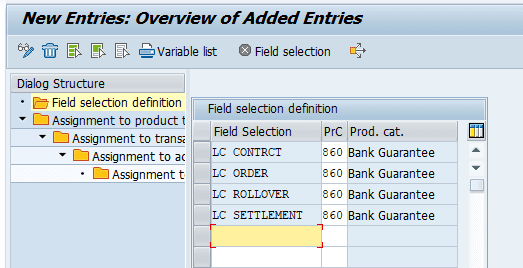
 Defining Field Selection
Defining Field Selection
In this step, you can set up the user interface for transaction management according to various criteria:
- All fields that are visible in the entry screens are grouped according to business criteria. For each field group, you can define whether it should be shown or hidden and whether the entries should be required or optional.
- You can also configure the various tabs in the transaction entry screens (such as administration or correspondence); you can set the tabs to hidden, optional entry or display only. However, you cannot define tabs as mandatory.
Exception: You cannot hide the
Structure tab.
 Accounting
Accounting
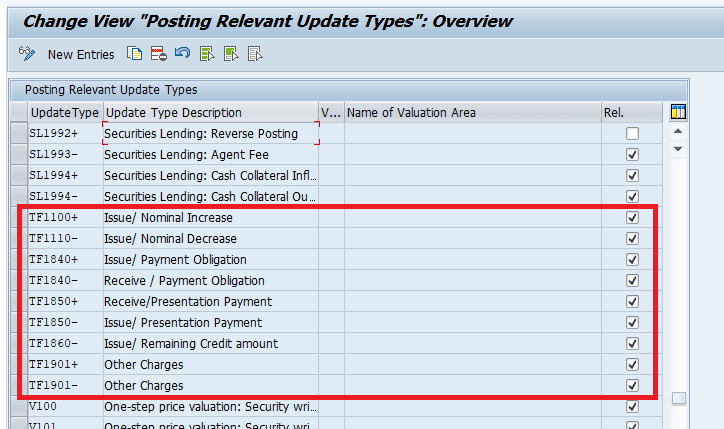
Indicate Update Types as Relevant to Posting.
In this IMG activity you specify (whether or not) the update type is relevant for posting.
This can depend on the valuation area. This means that you can post an update type in one valuation area and not in another.
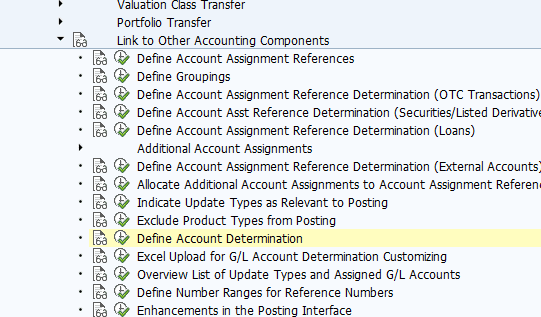
 Defining Account Determination
Defining Account Determination
You define the account determination settings for the flows in the parallel valuation areas. The account determination settings define the accounts to be used when the flows are posted to Financial Accounting.
The system only posts flows in the parallel valuation areas if an update type is set as relevant for posting under Indicate Update Types as Relevant to Posting and if posting specifications have been defined for the corresponding update types in this IMG activity.
 Enabling Position and Cash Management
Enabling Position and Cash Management
In the following activities, you make basic organizational settings for the parallel valuation areas.
You first define the valuation areas and accounting codes, and then assign them to each other. You also have the option of defining product categories not to be transferred to the parallel valuation areas.
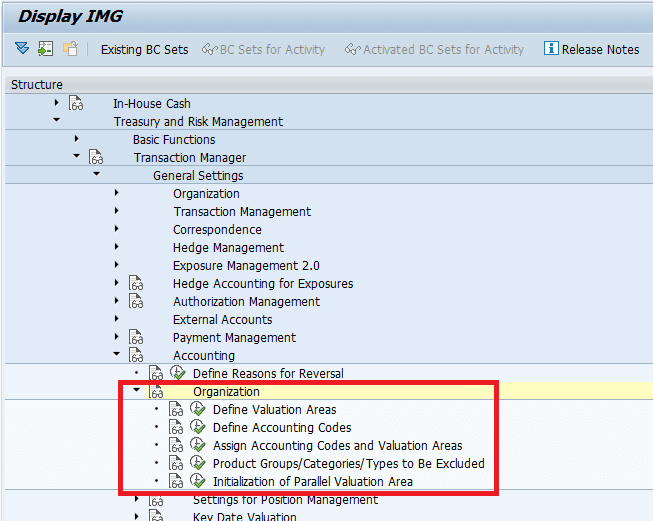 Settings for Position Management
Settings for Position Management
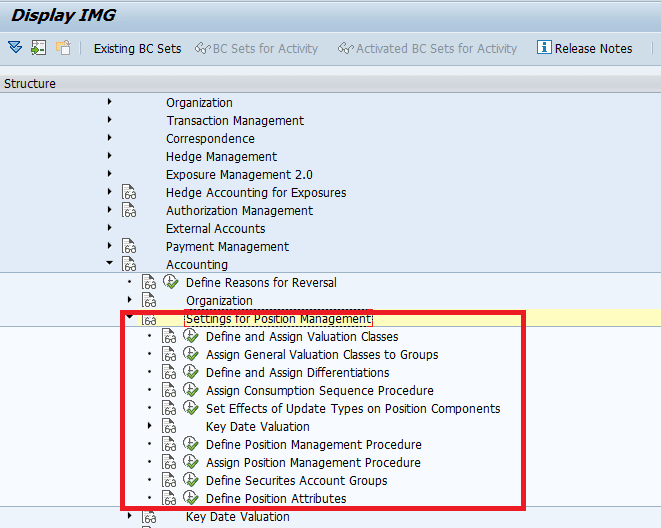 Link to Cash Management
Link to Cash Management
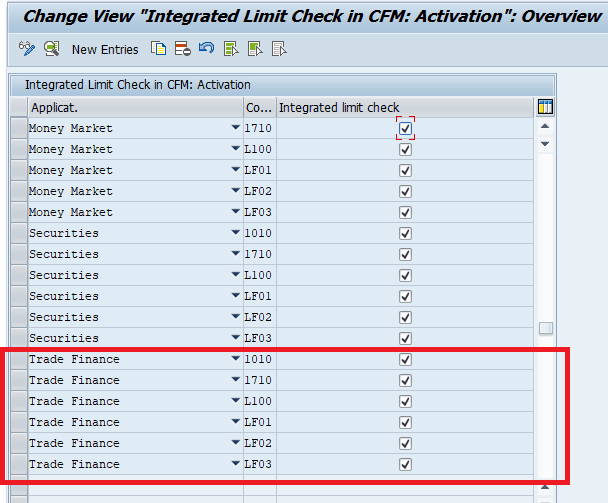
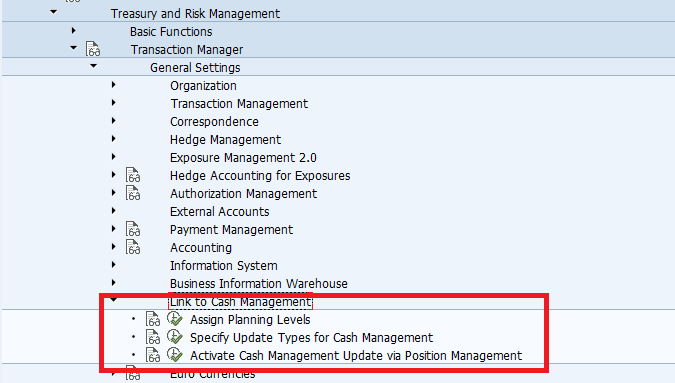 Enable Credit Risk Analyzer
Enable Credit Risk Analyzer
This component has the following functions:
- Quantifies different risk items relating to the market
- Assigns risks to their respective sources
- Allows you to control risks by assigning and monitoring limits
In this section, you can make all the system settings necessary for calculating risks and aggregating them according to different criteria.
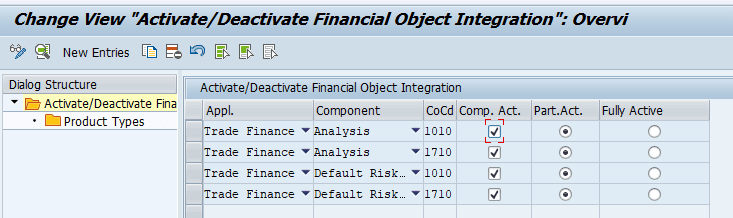
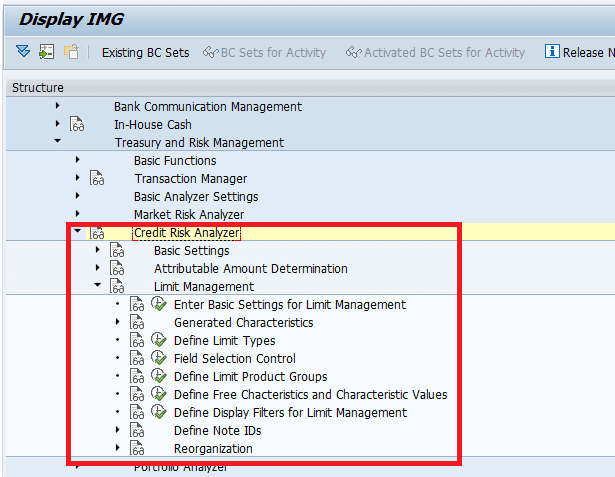 Activate/Deactivate Financial Object Integration
Activate/Deactivate Financial Object Integration
To be able to enter financial object data at the same time as you create master data, set the Component Active indicator. When you set this indicator, the system displays during online processing the relevant screens for entering transaction data for the component in question (such as Profitability Analysis and Default Risk Limitation). You can then enter the information required for the financial objects.
You can also define how the system reacts to errors. You can select:
- Completely Active if you do not want the system to save the master data for the transaction when there are errors.
- Partially Active if you want the system to save the master data but not the financial object part that is incorrect. In this case, a warning message is triggered when the system saves the data.
When you have made these settings on the company code level, you must then assign the product types for which these settings need to be active.
 Activate Integrated Default Risk Limit Check
Activate Integrated Default Risk Limit Check
 Summary
Summary
SAP S/4HANA Trade Finance Management helps you to better manage your Trade Finance instruments. This scope item supports common functionalities of Bank Guarantee, Letter of Credit and Stand by Letter of Credit. The system is able to capture the clear information classification with all details. The drawing and release facility can be automatically triggered based on the changes of the trade finance deal. Credit risk analyzer can be activated based on the product types with customizable limit rules and limit types. The utilization and release of limit can be triggered automatically from the deals themselves.
Preset status can cover the whole lifecycle of these financial instruments. You can configure approval processes for status changes and posting releases. In addition to functions for creating and changing Bank Guarantees/LC, the system also supports functions for rollover, contract settlement, and contract termination. Cash collateral and Bank Guarantee fees are also covered.
Stay tuned for my next blog post, where I will cover the following: –
- Integration with Sales
- Facility Management
- Correspondence
- Customization at BP level
- Use of Special G/L indicator
Author: Dinesh Kumar – Business and Technology Consultant – Finance and Risk Transformation
Need to hire SAP S/4HANA resources?
Looking for SAP S/4HANA work?
Get in touch with Eursap – Europe’s Specialist SAP Recruitment Agency
Source:
https://eursap.eu/2019/01/23/blog-trade-finances-sap-s4hana-treasury/


















































